Knee pain (KP) is a common musculoskeletal condition and a leading cause of disability in people over 50. It can be a short-term or long-term issue that requires medical care.
It is common in people of all ages, from active individuals to those less active. It can make daily activities like walking or climbing stairs harder, affecting quality of life.
Let us understand more about knee pain causes, symptoms, treatments, and management. Read on!
Anatomy of the Knee Joint
Your knee joint connects your thigh to your lower leg, where the thigh bone (femur) meets the shin bone (tibia). It includes cartilage for cushioning, ligaments for stability, and tendons that attach muscles to bones.
Together, these parts support your body and allow smooth movements like bending, straightening, and bearing the weight of your body with the support of your ankles and hips. You feel knee pain symptoms depending on the part or parts of your joint that are damaged.
Common Causes of Knee Pain
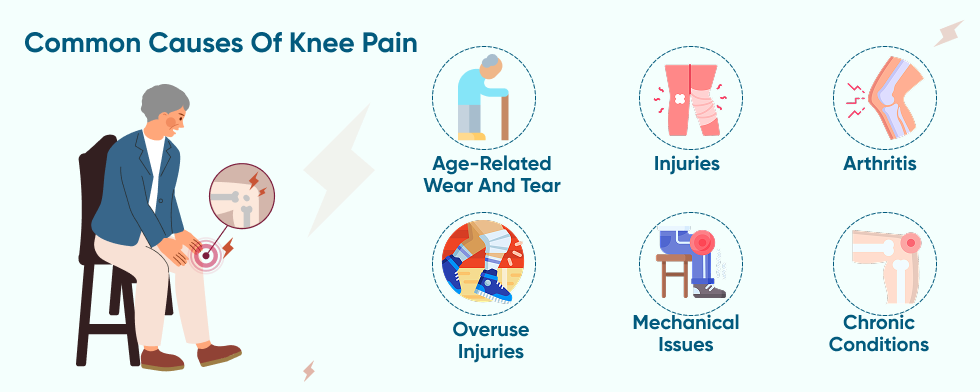
Temporary knee pain is mainly a result of an injury or accident, while chronic pain usually has multiple causes and rarely improves without treatment. Physical conditions or diseases are common culprits.
Common causes of knee pain depend on which part of the joint is affected and may include:
Age-related wear and tear:
- Joints naturally degenerate over time.
- According to the CDC, the chance of developing Osteoarthritis (OA) increases as people age.
- Cartilage is a rubbery material that cushions bones and allows smooth joint movement. As it wears down with age, bones can rub together, causing pain and tissue irritation. Severe degradation may lead to intense joint pain.
Injuries:
- Knee injuries that damage the joint can lead to pain.
- Common knee pain causes include repetitive strain, sports injuries, or trauma from falls or accidents.
- Some typical knee injuries are meniscus tears, ligament damage (ACL, MCL), or a dislocated kneecap (patellar dislocation).
Arthritis:
- Arthritis is a common cause of knee pain, leading to inflammation in the joint.
- It often causes symptoms like pain, swelling, and stiffness.
- Osteoarthritis(OA) is due to cartilage degeneration, Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is caused when your immune system attacks the tissue lining the joints, or gout arthritis is caused by the buildup of uric acid.
Overuse injuries:
- Physical activities, exercise, sports, and physical work can stress your knee.
- Repeating the same motions, like jumping or working with your hands and knees, can lead to knee pain.
- Tendinitis is a pain in the front of the knee that worsens with activities like climbing stairs or walking uphill, and bursitis is inflammation caused by repeated overuse or knee injury.
Mechanical issues:
- Loose fragments in the joint or iliotibial band syndrome (ITBS) (occurs when a tendon called the iliotibial band becomes irritated or swollen from rubbing against the bones in your hip or knee).
Chronic conditions:
- Patellofemoral pain syndrome (PFPS), knee pain under or around your patella (kneecap), causes long-term discomfort.
Symptoms of Knee Pain
- Knee pain can occur in different areas- the front, back, inside, or outside of the knee.
- Pain close to the surface above or behind your knee usually signals an issue with muscles, tendons, or ligaments.
- Pain deep inside your knee may come from bones or cartilage, whereas the radiating pain is in the lower leg or thigh, the back of the knee, or around it.
- You might also experience swelling, stiffness, instability, difficulty walking, bending, or engaging in physical activities.
How Knee Pain is Diagnosed
Knee pain is diagnosed through a medical history review and physical exam. Doctors may also use imaging tests like X-rays, MRIs, or ultrasounds to get a clear joint view.
- X-rays: Useful for finding fractures, dislocations, arthritis, or abnormal joint spaces.
- CT scans: A 3D X-ray for detailed images of fractures or deformities.
- MRI scans: These create 3D images to assess soft tissues like ligaments, tendons, and menisci, which X-rays and CT scans don’t show clearly.
Treatment Options for Knee Pain
The knee pain treatment is done based on its cause. The healthcare provider suggests treatment based on the pain severity and cause.
Conservative Treatments:
Medications:
- NSAIDs (pain relievers) like ibuprofen, aspirin, naproxen, or acetaminophen help to reduce the pain.
- The American College of Rheumatology (ACR) and the Arthritis Foundation (AF) strongly recommend corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation.
- The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved commercially available injectable corticosteroids– methylprednisolone, triamcinolone, betamethasone, and dexamethasone.
Physical therapy:
- A physical therapist would teach exercises to strengthen and stretch the knee. It improves your stability and helps with knee pain management.
Alternative therapies:
- Options like acupuncture or yoga improve flexibility and ease knee pain.
- A 2018 study found that regular yoga can help reduce knee arthritis symptoms, improve physical function, and boost overall well-being in people with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Non-Surgical Treatments:
PRP Therapy:
- Long-term use of NSAIDs and corticosteroid injections have systemic adverse effects and may cause joint cartilage destruction and flare-up of the osteoarthritic process.
- PRP injections can help people with knee osteoarthritis. It is a non-surgical, minimally invasive treatment.
- A small amount of your blood is processed to isolate platelet-rich plasma, which is injected into the target area to promote healing.
- Studies show PRP is effective in treating acute and chronic injuries, including bone, muscle, ligament, tendon, cartilage, OA, and nerve damage.
- Its advantages include biocompatibility, faster healing, safety, affordability, easy preparation, and proven clinical effectiveness. It helps manage pain and improve joint function.
- Since PRP uses your blood, the risk of allergic reactions or complications is low.
- Recent evidence suggests the benefit of PRP injections for the knee in mild to moderate osteoarthritis (OA) management. However, more studies need to be done.
Viscous injections:
- Knee Gel Injections (Viscosupplementation) provide cushioning in the knee joint.
- Hyaluronic acid is gel-like and naturally found in joints, reduces friction, and eases arthritis symptoms.
- Hyaluronic acid injections add lubrication to your knee joint.
Particulate steroids and non-particulate steroids:
- Particulate steroids are a type of corticosteroid injection used to reduce inflammation and pain in joints, are effective for arthritis, and provide longer-lasting relief compared to non-particulate steroids.
- Non-particulate steroid injection is designed for quick-acting relief of inflammation and pain. Unlike particulate steroids, they disperse quickly in the body, giving immediate but shorter-term relief in conditions affecting the knee or other joints.
Surgical Treatments:
- Severe injuries or arthritis may require surgery. Knee replacement (arthroplasty) or meniscus repair(surgery of a torn meniscus in the knee) are procedures done.
- The ligament reconstruction done for ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) tears is among the most common knee injuries that require reconstructive surgery.
When to See a Doctor
- You should see a doctor if you have constant knee pain.
- If the pain lasts longer than 3 weeks.
- If the pain is severe enough to change your daily routine or stop you from doing your usual activities.
- Consult a physical therapist or a sports medicine orthopedic specialist for further evaluation and treatment.
Conclusion
Addressing knee pain is crucial to prevent further damage and improve your quality of life. Exploring both non-surgical and surgical treatment options for knee pain treatment in Bangalore can help manage knee pain effectively and promote healing. PRP therapy is a promising knee pain treatment option in Bangalore that may offer relief and improve knee function.
If you are struggling with knee pain, we encourage you to consult Epione Pain Management Center in Bangalore for personalized knee pain treatment that suits your needs. Don’t wait. Take the first step toward recovery today!
Also Read:
1. How Proper Posture and Ergonomics Can Prevent Knee Pain
2. Top Exercises for Knee Pain Relief: Strengthen, Stretch, and Support Your Knees
3. Home Remedies for Knee Pain Relief: Natural Solutions You Can Try Today
4. Types of Knee Pain: Acute vs Chronic, How to Identify Them
5. Simple Lifestyle Changes to Prevent Knee Pain: Daily Habits for Healthier Joints
6. Knee Pain – Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment Options